The aggregate revenue of the public enterprises headquartered in China among the top 10 Asia-Pacific (APAC) cities, in terms of GDP, amounted to $8.4 trillion (47.9%) in 2022, finds GlobalData, a leading data analytics and research company.
An analysis of GlobalData’s Company Profiles Database reveals that five cities from China—Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Chongqing—featured in the list of top 10, followed by Japan with two cities—Tokyo and Osaka.
GlobalData ranked the cities based on the total revenue generated by the public companies headquartered in each city in 2022. The sample size considered for the research was about 29,000 public companies in the region.
The companies headquartered in the top 10 cities accounted for 55.2% of the aggregate revenue of the total sample size. The combined revenue of these companies grew year-on-year marginally by 0.3% in 2022.
Beijing was the largest city in terms of aggregate revenue contributed, followed by Tokyo and Seoul. Though Seoul and Singapore witnessed a strong year-on-year growth rate of 11.6% and 11% of revenue, respectively, in terms of average revenue per company, Beijing and Shanghai were the least among the top 10 APAC cities with $0.1 billion and $0.4 billion, respectively, in 2022.
Murthy Grandhi, Company Profiles Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “Easing of COVID-19 measures in China, along with a decline in property market activity and subdued worldwide demand, combined to yield sluggish economic expansion. However, China was the major revenue contributor in the APAC region with 26.5% share of the combined revenue of the listed companies.
Within China, Beijing was the major revenue contributor with 30.4% share, followed by Shanghai (8.7%), and Shenzhen (6.6%) in 2022. In terms of year-on-year revenue growth, Beijing witnessed 2.6% growth and Guangzhou witnessed a decline of 5.5%.
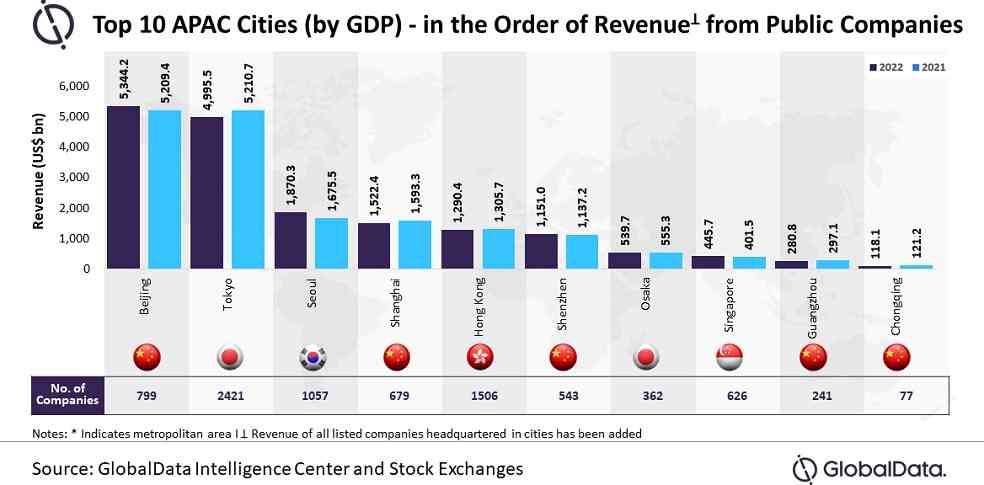
According to GlobalData’s economic research, the top 10 cities were home to more than 8,000 companies (about 28.3% of the sample size). About 29.1% of these were based out of Tokyo, followed by Hong Kong (18.1%), Seoul (12.7%), Beijing (9.6%), Shanghai (8.2%), Singapore (7.5%), Shenzhen (6.5%), Osaka (4.4%), Guangzhou (2.9%), and Chongqing (0.9%).
Grandhi concludes: “As we navigate the complex economic conditions, it is evident that the resilience and adaptability of Chinese enterprises remain instrumental in driving growth. Despite challenges, this data showcases China’s enduring impact on the Asia-Pacific business landscape.”
LATEST NEWS | China Reaffirms Sino-Venezuelan Ties: A New Era of Cooperation



